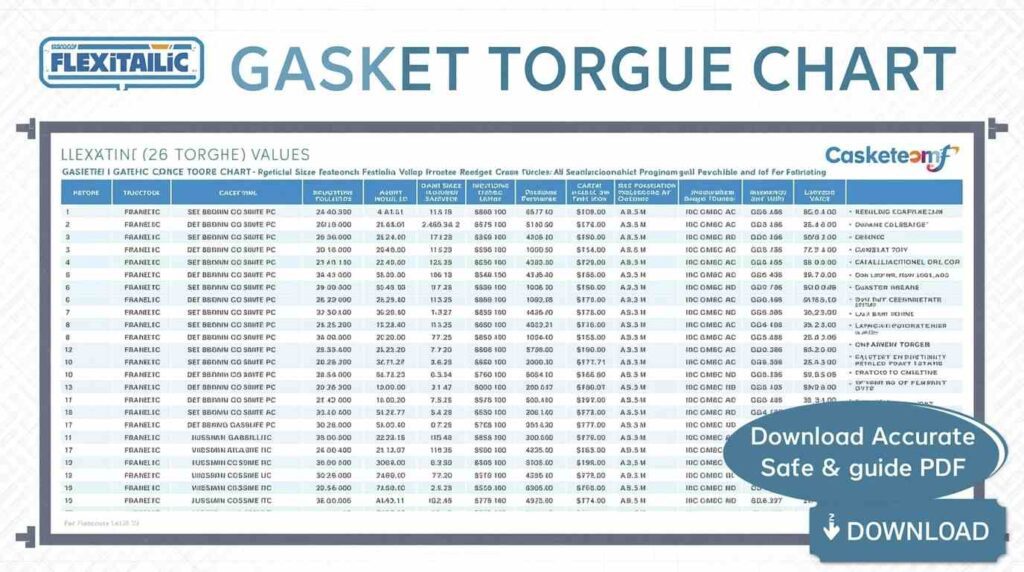
Introduction about Flexitallic Gasket Torque Chart
Working with flanges and gaskets can be tricky if you don’t know the proper torque specifications. The flexitallic gasket torque chart is a reliable guide that ensures flanges are tightened correctly, avoiding leaks and equipment damage. Using the right torque helps maintain safety and efficiency in pipelines and industrial systems. Engineers and maintenance technicians rely on charts like this for quick reference during installation and inspections. In this guide, we will explore how to read the Flexitallic torque chart, compare it with other charts like Lamons spiral wound gasket torque chart, Garlock gasket torque chart, and RTJ gasket torque chart, and explain practical tips for safe and accurate use.
Why Flexitallic Gasket Torque Charts Are Essential
A torque chart provides precise bolt tightening values for specific gaskets and flange sizes. Without following these charts, even experienced technicians risk uneven pressure, leaks, or flange damage. The flexitallic gasket torque chart is designed to simplify this process, giving clear torque ranges for various flange classes and sizes. It removes guesswork and improves safety.
Using a chart also improves consistency across teams. For example, in industrial plants, multiple engineers might work on the same pipeline. With the chart, everyone applies the same torque, preventing common maintenance errors. It’s like following a recipe in cooking; the right measures yield perfect results every time.
How to Read a Flexitallic Torque Chart Correctly
Flexitallic torque charts list flange size, gasket type, and recommended torque values in pounds per inch or Newton meters. Each column provides minimum and maximum torque, ensuring bolts are neither too loose nor too tight. Understanding units and flange class is key. Engineers can quickly find the correct torque for Flexitallic CG gaskets or CGI gasket torque charts using this system.
Reading the chart also involves knowing the bolt material and lubrication. Torque values change depending on whether bolts are lubricated or dry. Failing to consider this can result in under-tightening or over-tightening. Real-world experience shows that taking two minutes to cross-check units prevents costly leaks and downtime.
Comparing Lamons Spiral Wound Gasket Torque Chart
Lamons spiral wound gaskets are another popular choice in industrial piping. Their torque chart resembles the Flexitallic chart but includes specific guidance for different materials like stainless steel or carbon steel. Comparing these charts helps engineers make informed choices when substituting gasket types.
Many technicians prefer Flexitallic for quick reference due to its clear formatting. However, understanding Lamons charts can be helpful when working on retrofits or when replacement gaskets are not Flexitallic. Think of it like choosing the right tire for a car; charts help match specifications precisely.
Read More About: Flexitallic Gasket Torque Chart
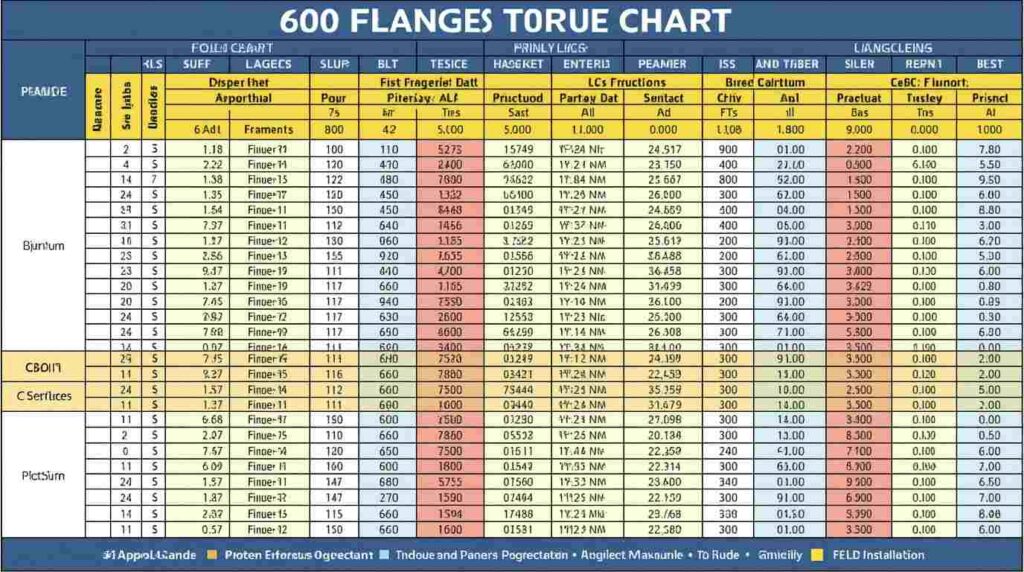
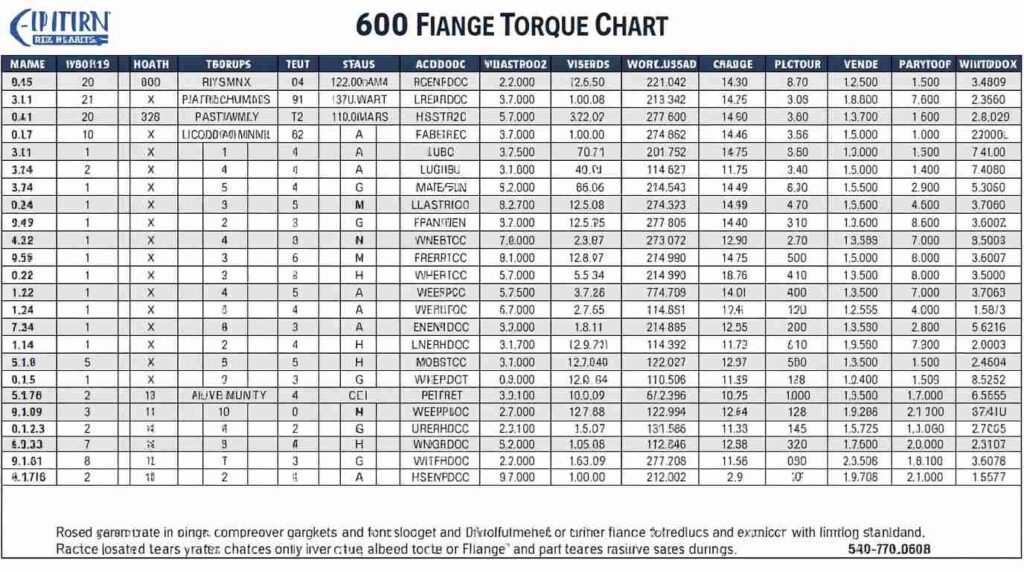
Using 600 Flange Torque Chart PDF in Practice
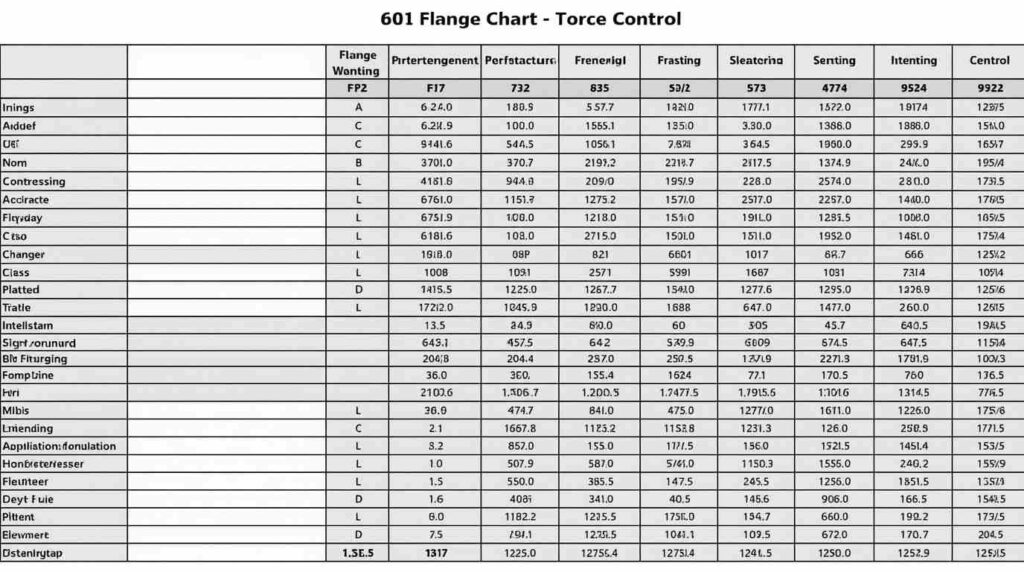
Large industrial flanges, such as 600-class, require careful torque control. The 600 flange torque chart PDF is often used for high-pressure applications. Engineers refer to this PDF to avoid over-compressing gaskets and risking leaks or flange warping.
In practice, technicians can print or save the PDF for field use. Having this chart accessible ensures accuracy and saves time. During audits, teams often show charts like these to prove compliance with installation standards, making documentation easier and reducing errors.
Garlock Gasket Torque Chart Overview
Garlock gaskets are widely used in chemical, oil, and gas industries. Their torque charts provide values for spiral wound and compressed gaskets. Understanding the differences between Garlock and Flexitallic torque charts is essential when swapping gasket types.
Many maintenance teams keep both charts handy. Using the correct chart reduces the risk of leaks, which can be costly and dangerous. Proper torque ensures gasket seating without over-compression, similar to tightening a jar lid just right—too loose or too tight both cause problems.
Spiral Wound Gasket Torque Chart Tips
Spiral wound gaskets are sensitive to torque values due to their layered construction. Over-tightening can crush inner windings; under-tightening can lead to leakage. The spiral wound gasket torque chart helps engineers maintain the right balance, optimizing sealing performance.
Experienced engineers often combine the chart with a feel test. They use a torque wrench to follow chart values and visually inspect flange alignment. This combination ensures the gasket performs correctly under operational pressure, extending its service life.
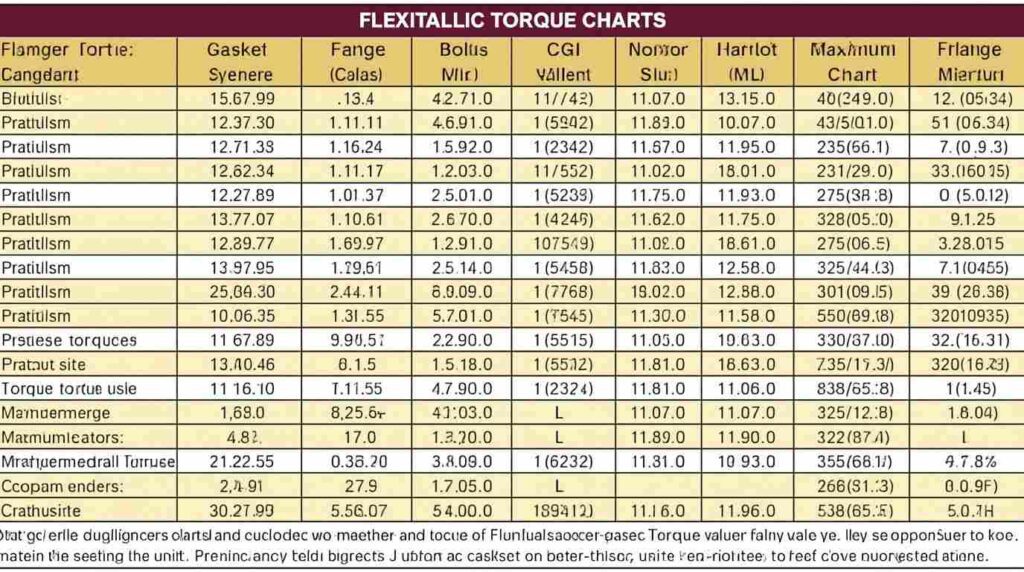
Understanding Flexitallic CG Gasket Specifications
Flexitallic CG gaskets are a type of spiral wound gasket designed for high-pressure, high-temperature applications. Torque charts specific to CG gaskets provide minimum and maximum bolt values to prevent failure.
CG gaskets require attention to flange material, bolt size, and lubricant. Using the torque chart correctly prevents leaks in critical systems. For example, in steam pipelines, improper torque can lead to safety hazards and downtime, emphasizing the importance of accurate readings.
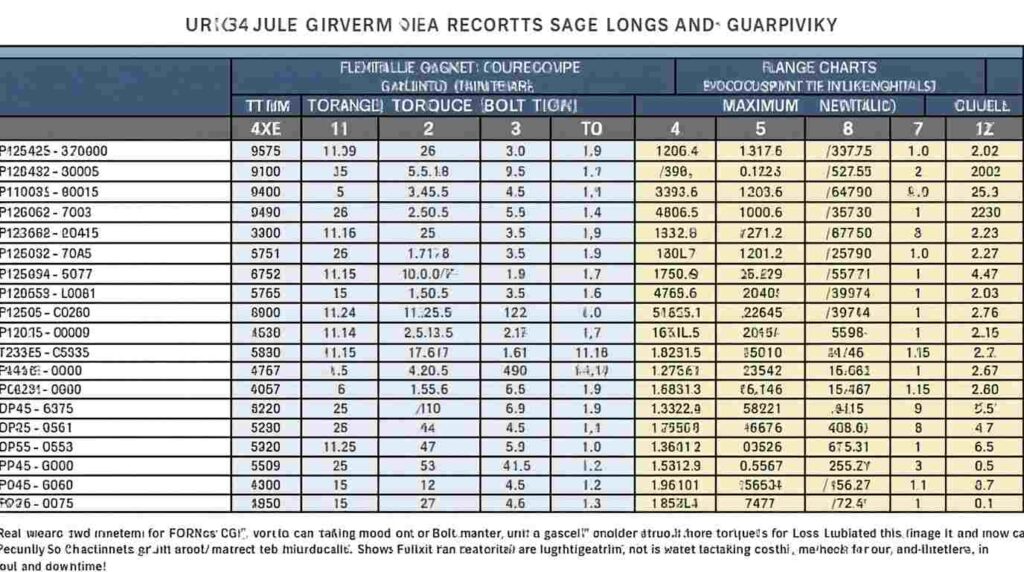
RTJ Gasket Torque Chart Insights
Ring Type Joint (RTJ) gaskets need precise torque to seat properly in flanges. The RTJ gasket torque chart gives guidance for various flange sizes and classes. Following these charts ensures metal-to-metal contact, maintaining a strong seal under high pressure.
RTJ gaskets are common in refineries and high-pressure pipelines. Engineers often cross-reference Flexitallic and RTJ charts for hybrid systems. Using torque charts reduces guesswork, ensuring reliable sealing and long-term operational safety.
Common Mistakes When Using Torque Charts
Many technicians ignore lubrication, bolt material, or unit conversions when using torque charts. Overlooking these details can lead to leaks or damaged flanges. Using the flexitallic gasket torque chart carefully helps prevent these mistakes.
Another common mistake is assuming all spiral wound gaskets behave the same. Charts like Garlock and Lamons highlight material differences. Following the correct chart for the specific gasket ensures safety, efficiency, and longevity of the system.
Practical Applications and Field Tips
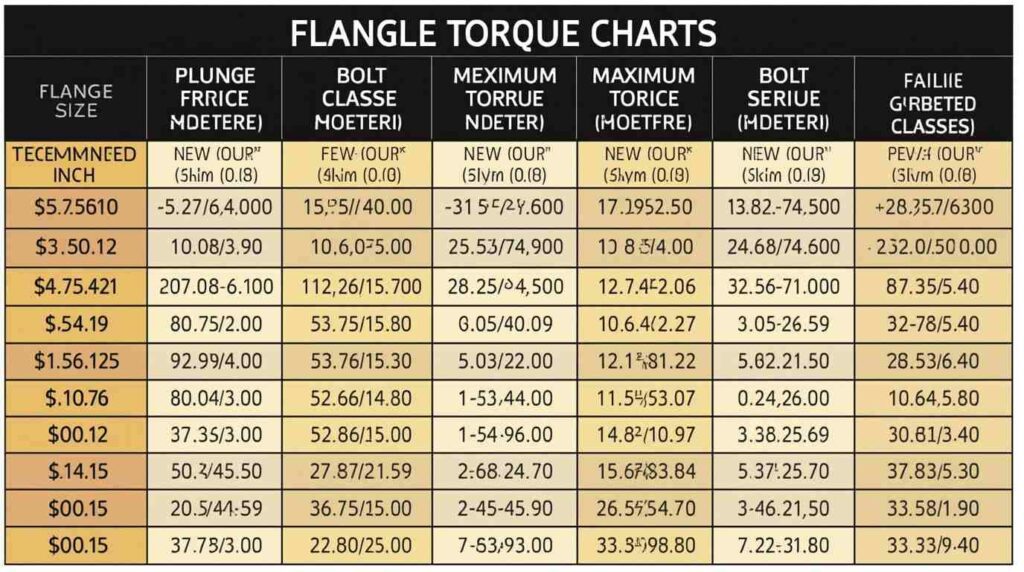
Torque charts are not just theoretical tools—they are used daily in oil, gas, chemical, and power plants. Engineers use the charts while installing, maintaining, or inspecting piping systems. Keeping printed PDFs or digital charts on mobile devices allows quick access on-site.
Field tips include checking bolt threads, cleaning flange faces, and pre-lubricating bolts if specified. Combining these practices with torque chart guidance ensures reliable installations. Accurate torque improves safety, reduces downtime, and saves costs over time.
Conclusion for Flexitallic Gasket Torque Chart
The flexitallic gasket torque chart is a critical tool for engineers and maintenance technicians. It provides precise torque values for various gaskets and flanges, ensuring safety and preventing leaks. Comparing it with Lamons, Garlock, and RTJ charts helps in selecting the right gasket and torque for specific applications. Using the chart properly, along with field checks and lubrication guidance, improves accuracy, efficiency, and equipment longevity. For anyone working with spiral wound gaskets, keeping this chart handy is like having a map in unfamiliar terrain—it guides every bolt and guarantees reliable results under pressure.
Also Visit To Gasket
FAQs About Flexitallic Gasket Torque Chart
What is a Flexitallic gasket torque chart?
A Flexitallic gasket torque chart is a reference guide that provides recommended bolt torque values for different gaskets and flange sizes. It helps engineers apply the correct pressure when installing spiral wound, CG, or RTJ gaskets. Following the chart prevents leaks, flange damage, and safety hazards. Think of it like following a recipe—too little or too much torque can spoil the seal.
The chart typically lists flange classes, bolt sizes, lubrication conditions, and torque values in either pounds per inch or Newton meters. Using the chart ensures consistency, especially when multiple technicians work on the same system.
Why is using a torque chart important?
Torque charts are essential for safety, performance, and longevity of piping systems. Over-tightening bolts can crush the gasket, while under-tightening can lead to leaks. A Flexitallic gasket torque chart provides accurate ranges, reducing guesswork. It is widely used in chemical, oil, and gas industries where precision matters.
Using charts also improves efficiency. Engineers can quickly reference recommended values during installation or maintenance, saving time and reducing human error. It ensures the system remains reliable under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Can I use Flexitallic charts with other gaskets?
Yes, but carefully. Flexitallic charts are designed for their own gaskets, like Flexitallic CG or spiral wound gaskets. Other charts, such as Lamons spiral wound gasket torque chart, Garlock gasket torque chart, or RTJ gasket torque chart, provide values for different materials or designs.
If substituting gaskets, cross-reference the correct chart to avoid under- or over-torquing. Each chart accounts for material differences, flange class, and bolt lubrication, so using the wrong chart can compromise safety.
How do I read the chart correctly?
Start by identifying the flange size and class, then locate the bolt size. Check the recommended torque for dry or lubricated bolts. Charts often provide minimum and maximum torque values, ensuring bolts are neither too loose nor too tight.
Always use a calibrated torque wrench, and consider material properties and environmental conditions. Proper reading ensures the gasket seats evenly, preventing leaks and extending service life.
Are PDF versions of torque charts reliable for field use?
Yes. PDFs like the 600 flange torque chart PDF can be printed or stored digitally. They provide easy access on-site for engineers and maintenance teams. Having a PDF ensures consistency, allows quick reference, and supports compliance documentation.
It’s best to keep both Flexitallic and other relevant charts accessible to handle different gasket types during installation or inspection.